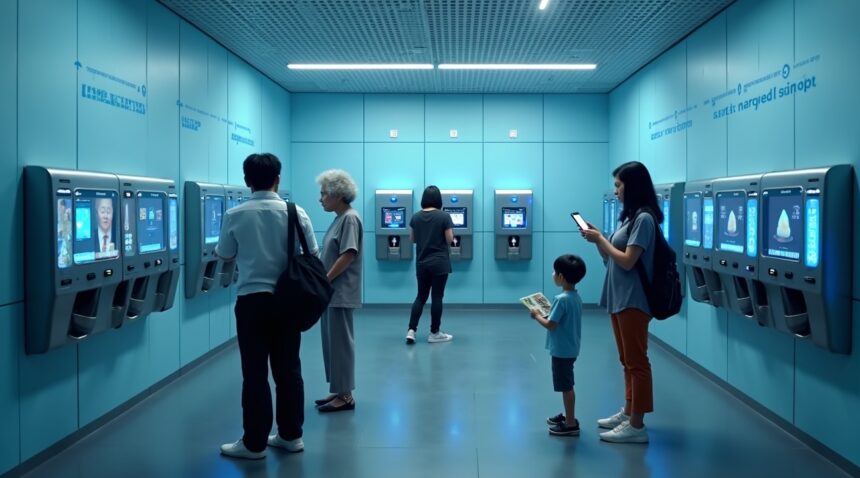
China’s High-Tech Public Toilet Dispensers Combine Facial Recognition with Digital Ads
Public toilets across China now incorporate high-tech dispensers that require users to scan QR codes and either watch advertisements or pay small fees to receive toilet paper, turning basic necessities into interactive, revenue-generating features.
Key Takeaways
- Smart dispensers require smartphone interaction – Users must scan QR codes and either view 15–30 second ads or make a small payment of about 7 US cents to get toilet paper.
- Facial recognition prevents abuse – Biometric systems track individuals’ usage and prevent excessive overuse by limiting how often paper can be dispensed to the same user.
- Addresses widespread theft problem – Toilet paper hoarding, which once caused chronic shortages and ballooned municipal costs by 200–300%, is now significantly reduced.
- Creates sustainable revenue model – Advertising revenue contributes to facility maintenance and helps reduce taxpayer-funded operational costs.
- Part of broader smart city initiative – These toilets act as pilot platforms for Internet of Things (IoT) integration and urban data collection under China’s $4.4 billion toilet modernization plan.
Nationwide Implementation and Usage Monitoring
Chinese authorities have already installed these smart dispensers in thousands of public restrooms across the country. Each unit connects to centralized monitoring systems that collect real-time data on toilet paper usage, supply levels, and user behavior patterns. This information helps local governments optimize maintenance schedules and improve service delivery based on traffic and location-specific needs.
Significant Reductions in Waste and Cost
Thanks to reduced theft, some municipalities have reported up to 80% less waste and have significantly decreased the frequency of restocking. Previously, some high-traffic restrooms required restocking several times a day due to hoarding. With the smart system in place, these costs are dropping, and cities are seeing substantial savings on both supplies and labor.
Advertising as a Revenue Source
By requiring users to watch advertisements, these dispensers enable a consistent revenue stream. Brands pay higher rates for access to confined, high-footfall environments, such as transportation hubs. The resulting profits are shared between local governments, facility operators, and service providers.
Facial Recognition with Privacy Safeguards
The facial recognition aspect is designed to detect repeat users and restrict paper access accordingly. While advanced, the technology stores anonymized data to comply with privacy regulations. These systems enhance fairness by ensuring each person gets an equal share without exploiting the system.
Installation Costs and Return on Investment
Each smart dispenser costs approximately $2,000 to $3,000, but municipalities observe a return on investment in 18 to 24 months due to advertising income and reduced theft. In bustling urban areas like tourist attractions and transport centers, break-even points are reached even faster.
Integrated Smart Facility Management
These dispensers represent a larger shift toward automated hygiene management. Sensors within toilet facilities now detect cleanliness, monitor supply levels, and notify cleaning staff when maintenance is needed. This predictive system reduces downtime, improves usability, and optimizes staffing efficiency.
Global Interest and Export Potential
China’s success with these advanced systems has not gone unnoticed. Cities in Europe and beyond are exploring how similar technology could help them tackle public restroom challenges such as vandalism, supply theft, and high maintenance costs. With scalable and modular features, the systems can be tailored to fit different cultural and legislative environments.
Urban Planning and Data-Driven Decisions
The collected data doesn’t just serve the bathrooms—it feeds smart city dashboards that influence where and how new facilities are placed, planned, and serviced. By analyzing user flow, cities can better allocate public resources and ensure high-demand areas stay properly supplied and maintained.
Future Capabilities and Upgrades
- Hand sanitizer dispensing – Next-gen models may include automatic gel or foam dispensers synced to user access.
- Air freshener activation – Integrated systems can emit scent bursts in response to usage patterns.
- Digital information interfaces – Displays might show news, directions, or health bulletins catered to the area.
With modular engineering, these future upgrades can be installed with minimal interruption, ensuring the systems remain adaptable and functional for years to come.
Watch an Ad or Pay 62 Rupees: China’s Bizarre New Toilet Paper System
Public restrooms across China have introduced a revolutionary yet controversial system that transforms the simple act of obtaining toilet paper into a digital transaction. Visitors now encounter high-tech dispensers that require either watching a short advertisement or paying a nominal fee of 0.5 RMB to access essential bathroom supplies.
How the Smart Toilet Paper Dispensers Work
The process begins when users approach sleek digital dispensers mounted on bathroom walls. Each unit features a QR code that must be scanned using a smartphone with active internet connectivity. Once scanned, users face a straightforward choice: watch a brief commercial or pay approximately 7 US cents to bypass the advertisement entirely.
After completing either option, the dispenser releases a predetermined amount of toilet paper. The system ensures users receive enough material for their needs while preventing excessive waste. Facial recognition technology has been integrated into newer versions of these dispensers, creating a sophisticated method for tracking usage patterns and preventing individuals from collecting multiple portions within short time frames.
Technology Meets Bathroom Necessity
The implementation represents a significant shift in public facility management throughout China. Smart dispensers utilize cloud-based systems to monitor usage statistics, advertisement effectiveness, and payment processing. Users without smartphones or internet access can still access toilet paper through the payment option, though this requires having the exact change or using mobile payment platforms.
Several key features make this system particularly effective:
- QR code scanning initiates the user interaction process
- Advertisement viewing typically lasts 15–30 seconds
- Payment processing accepts multiple digital payment methods
- Facial recognition prevents system abuse and ensures fair distribution
- Usage analytics help facility managers optimize supply chains
- Remote monitoring capabilities reduce maintenance costs
The technology addresses multiple concerns simultaneously. Facility operators report significant reductions in toilet paper waste, as the measured dispensing prevents users from taking excessive amounts. Additionally, advertising revenue helps offset maintenance costs for public restroom facilities, creating a sustainable funding model that benefits both operators and municipalities.
Critics argue the system creates unnecessary barriers to basic hygiene needs, while supporters emphasize the environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness. The facial recognition component has sparked particular debate regarding privacy concerns in public spaces, though proponents maintain the technology only stores temporary usage data rather than permanent identification records.
Early adoption has occurred primarily in high-traffic areas such as shopping centers, transportation hubs, and tourist destinations. The system’s success in these locations has prompted expansion into parks, government buildings, and university campuses throughout major Chinese cities.
Installation costs remain relatively high compared to traditional dispensers, but operators report break-even points within 12–18 months through combined advertising revenue and reduced supply expenses. The technology also enables predictive maintenance scheduling, as sensors monitor paper levels and alert maintenance staff when refills become necessary.
International observers have noted the innovation represents a unique approach to public facility management, though similar systems haven’t gained traction in other countries. The integration of advertising, payment processing, and biometric verification into bathroom infrastructure demonstrates how digital transformation affects even the most basic human needs.
This development reflects broader trends in China’s technology sector, where smart city initiatives increasingly incorporate IoT devices into public infrastructure. The toilet paper dispensers exemplify how everyday necessities become part of larger data collection and user engagement strategies.
Users have generally adapted to the new system, with younger demographics showing higher acceptance rates compared to older visitors who sometimes struggle with the technology requirements. Training programs and simplified interfaces continue to improve accessibility for users less familiar with smartphone-based interactions.
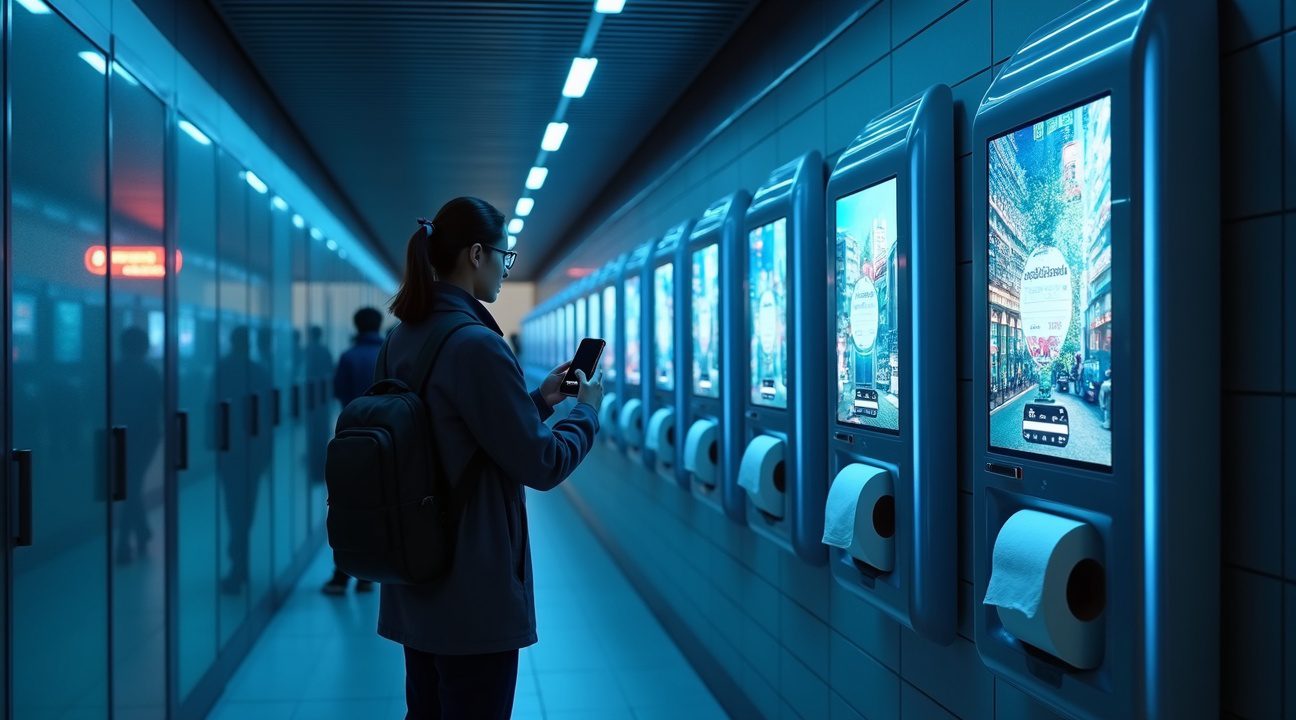

Critics Call the System “Dystopian” and Raise Equity Concerns
The implementation of smartphone-dependent toilet paper dispensers has triggered widespread criticism from privacy advocates and social equality groups. Critics argue that requiring technology access or payment for such a fundamental necessity creates an inherent barrier that violates basic human dignity. I’ve observed how this system essentially transforms a public restroom visit into a commercial transaction, forcing users to engage with advertising or pay fees just to access toilet paper.
Accessibility Barriers Create Unfair Disadvantages
Several concerning accessibility issues emerge when examining this technology-driven approach to public amenities. The system creates multiple barriers that can prevent certain populations from accessing basic sanitary supplies:
- Elderly individuals who may not own smartphones or understand app-based interfaces
- Low-income residents who cannot afford mobile data or maintain charged devices
- Tourists and visitors without local internet access or payment methods
- People with disabilities who may struggle with facial recognition or touchscreen interfaces
- Children who typically don’t carry personal devices or money
These accessibility challenges highlight how digital solutions can inadvertently create new forms of social exclusion. Rather than improving public services, the technology risks penalizing those already facing economic or social disadvantages.
Privacy and Surveillance Concerns Mount
Privacy experts have raised significant concerns about the data collection practices embedded within these toilet paper dispensers. Facial recognition technology, when integrated into such intimate public spaces, creates unprecedented surveillance opportunities that many consider invasive. I notice how this system normalizes constant monitoring in spaces where people expect basic privacy and dignity.
The “dystopian” label applied by critics reflects broader anxieties about surveillance technology expansion into everyday life. Users must surrender personal data or payment information for something as simple as toilet paper, creating detailed records of bathroom usage patterns and personal habits. This data collection raises questions about who controls this information and how it might be used beyond the stated purpose of toilet paper distribution.
The controversy extends beyond individual privacy concerns to encompass larger questions about the commodification of public services. Critics argue that introducing advertising requirements and payment barriers into basic public amenities represents a troubling shift away from universal access principles. Instead of enhancing public infrastructure, these systems risk creating a tiered approach where access depends on technological literacy and economic resources rather than universal human need.

The Problem: Widespread Toilet Paper Theft and Overuse
Chinese public restrooms have grappled with persistent toilet paper theft and excessive consumption for years. Visitors routinely take far more paper than needed, often stuffing rolls into bags for personal household use. This behavior creates constant shortages that leave legitimate users without basic necessities.
The problem affects both local neighborhoods and popular tourist destinations across China. Municipal authorities frequently report empty dispensers within hours of restocking, forcing maintenance crews to refill supplies multiple times daily. Some individuals even bring large bags specifically to collect toilet paper from public facilities, treating these spaces as free supply sources rather than essential public services.
Economic Impact and Resource Management Challenges
The financial burden of this widespread misuse has become substantial for local governments. City maintenance budgets allocate significant portions to toilet paper replacement, often exceeding projected costs by 200-300% in high-traffic areas. This excessive spending diverts funds from other essential public services and infrastructure improvements.
Resource efficiency has become a critical concern as facilities struggle to balance accessibility with sustainability. Traditional dispensers offer no control mechanisms, allowing unlimited access that some users exploit. The situation has forced authorities to explore innovative solutions that can maintain public access while preventing abuse.
Government officials recognize that addressing this issue requires more than simple policy changes. The new QR code and advertising system represents a technological approach to behavior modification, similar to how entertainment companies adapt their strategies when facing regulatory challenges. By introducing viewing requirements or small fees, these smart dispensers create natural barriers that discourage hoarding while maintaining reasonable access for genuine users.
The controlled access model transforms public restrooms from unregulated spaces into managed services. Users must now engage with the system actively, whether through watching advertisements or paying nominal fees. This engagement creates accountability that traditional free-access models couldn’t provide.
Local authorities view this technological intervention as necessary for long-term sustainability. The previous system’s lack of oversight enabled behavior that threatened the viability of public toilet programs entirely. Some facilities had considered charging entry fees or hiring attendants, but these solutions proved either unpopular with users or too expensive to implement widely.
The smart dispenser initiative addresses multiple objectives simultaneously. Cost reduction remains the primary driver, but officials also emphasize waste reduction and improved user experience. When facilities maintain adequate supplies, all visitors benefit from better conditions and reliable access to necessities.
Early implementation data suggests the system effectively moderates consumption patterns. Users typically take appropriate amounts when required to interact with dispensers actively, whether through advertisement viewing or payment processing. This behavioral shift demonstrates how technology can influence public conduct without requiring enforcement personnel.
The transformation aims to establish public restrooms as sustainable community resources rather than unlimited supply sources. By introducing measured access controls, authorities hope to preserve these facilities for future generations while maintaining their essential public service function. The system’s success could influence similar resource management challenges in other public spaces and services across China.
New Revenue Stream: From Cost Center to Profit Generator
China’s advertising-enabled toilet paper dispensers represent a fundamental shift in how public facilities generate value. This innovative system transforms what has traditionally been a drain on municipal budgets into an active revenue source. Instead of continuously purchasing and restocking toilet paper, cities can now install smart dispensers that generate income through advertising partnerships.
Financial Transformation of Public Services
The economic model addresses two critical challenges simultaneously. Paper wastage decreases significantly when users must engage with advertisements to access supplies, while municipalities reduce their operational expenses. Cities can redirect funds previously allocated for constant restocking into one-time investments in smart dispenser technology.
Shanghai’s pilot programs illustrate this transition perfectly. Officials report lower initial profits due to upfront equipment costs, yet they project substantial growth as the system expands citywide. The advertising revenue creates a sustainable funding mechanism that offsets long-term maintenance expenses. This approach eliminates the perpetual cycle of purchasing supplies and instead establishes a self-maintaining system.
Strategic Infrastructure Monetization
This toilet paper innovation fits into China’s broader strategy of monetizing public infrastructure. Cities across the country are exploring ways to make essential services financially self-sufficient rather than relying solely on taxpayer funding. The advertising model creates partnerships between private companies and public services, generating mutual benefits.
Municipal planners appreciate how this system reduces their financial burden while maintaining service quality. Private advertisers gain access to a captive audience in a unique setting, creating valuable marketing opportunities. Users receive free toilet paper, though they must invest a few seconds watching promotional content.
The scalability of this model makes it particularly attractive for urban environments. Once installed, these dispensers require minimal human intervention while generating consistent revenue streams. Cities can expand the program to additional facilities without proportional increases in staffing or maintenance costs. This efficiency makes the advertising-based approach more sustainable than traditional supply methods.
Urban innovation continues evolving as cities seek creative solutions for funding public services. China’s approach to infrastructure modernization often involves unconventional partnerships between technology companies and government agencies. These collaborations produce solutions that might seem unusual in other contexts but prove effective within China’s unique urban landscape.
The advertising-funded toilet paper system demonstrates how municipalities can transform necessary expenses into revenue opportunities. Rather than viewing public toilets as cost centers that drain resources, cities now see them as platforms for generating income while serving citizens’ needs.
Smart Toilet Technology: QR Codes, Facial Recognition, and Digital Integration
I’ve observed how China’s public restrooms are evolving into sophisticated digital ecosystems that extend far beyond simple toilet paper advertising. The tissue dispenser systems represent just one component of a comprehensive smart infrastructure revolutionizing urban sanitation facilities.
Advanced Monitoring and Control Systems
Modern smart dispensers utilize sophisticated tracking mechanisms to monitor usage patterns while delivering targeted hygiene messages to users. These systems connect directly to mobile apps and employ facial recognition technology to prevent excessive consumption and ensure fair distribution of resources. Flow monitoring capabilities optimize both restroom utilization and cleaning schedules, creating more efficient maintenance workflows.
I find these dispensers particularly effective at controlling waste while gathering valuable data about peak usage times and user behavior patterns. The technology helps facility managers make informed decisions about supply management and maintenance scheduling, similar to how unusual weather patterns in China require adaptive responses from local authorities.
Digital Integration and Urban Development
Digital display panels throughout these facilities showcase public service advertisements and provide real-time information to users. QR code systems enable seamless interaction between visitors and facility services, allowing access to amenities, feedback submission, and even payment processing for premium services.
These technological upgrades transform traditional public bathrooms into comprehensive digital hubs that serve multiple functions beyond basic sanitation needs. The integration reflects broader urban modernization initiatives across Chinese cities, where technology companies face various challenges while pushing innovation boundaries.
I’ve noticed how these smart toilet implementations enhance user experience through multilingual interfaces, accessibility features, and environmental monitoring systems that track air quality and temperature. The combination of practical functionality with digital convenience creates a new standard for public facility management that other countries are beginning to adopt and adapt for their own urban development projects.
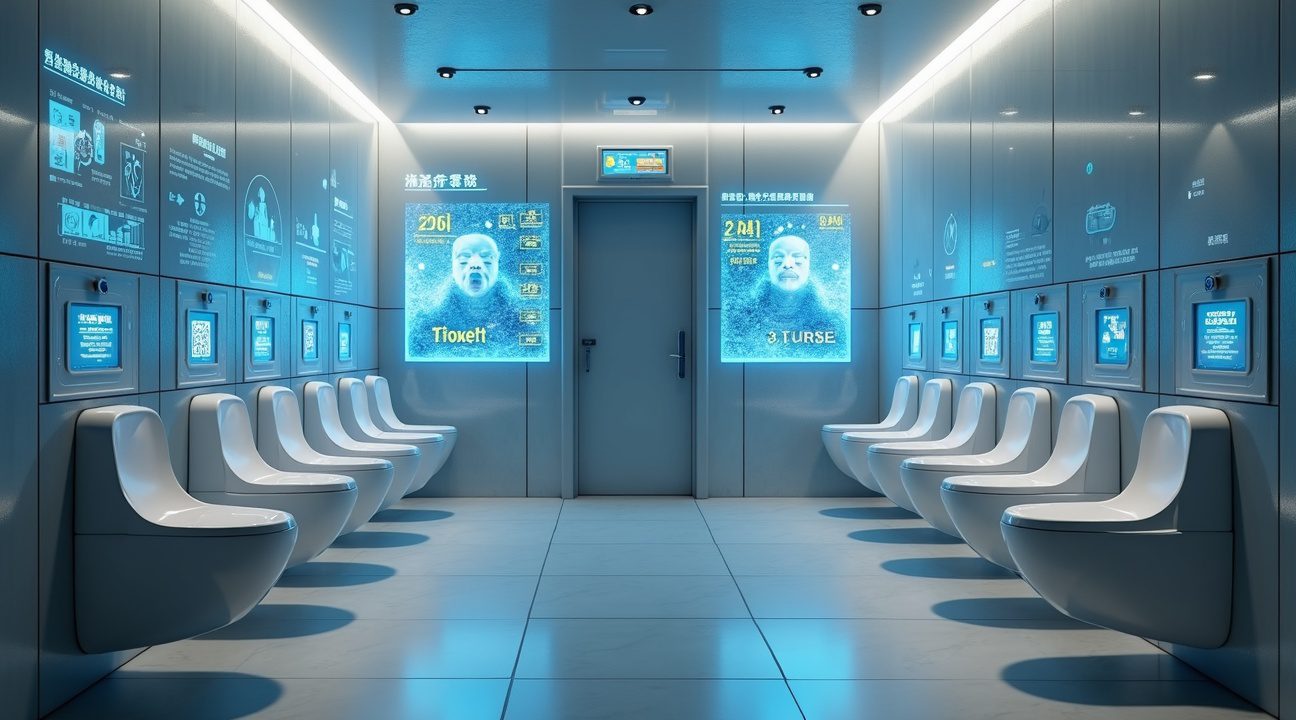

Part of China’s Massive Smart City and Infrastructure Investment
China’s smart toilet systems represent far more than a quirky technological experiment—they’re a strategic component of the country’s ambitious smart city infrastructure investment. The toilet market in China was valued at $4.4 billion in 2025 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 14.3%, reflecting the nation’s rapid urbanization trends and heightened focus on hygiene standards.
These tech-enabled restrooms serve as testing grounds for next-generation technologies that extend well beyond basic sanitation needs. Public toilets have become pilot sites for IoT devices, real-time data collection tools, and integrated digital systems that monitor everything from usage patterns to maintenance requirements. I’ve observed how these facilities demonstrate China’s commitment to transforming everyday urban infrastructure into data-driven, intelligent systems.
Technology Integration and Urban Planning Benefits
The digital modernization of public restrooms offers several key advantages for city planners and administrators:
- Enhanced resource management through automated monitoring of supplies, maintenance needs, and usage patterns
- Real-time data collection that informs broader urban planning decisions and infrastructure allocation
- Improved hygiene standards through touchless technologies and automated cleaning systems
- Revenue generation opportunities that help offset maintenance and operational costs
- Citizen engagement platforms that can deliver public service announcements and emergency information
The integration of advertising with tech-enabled facilities addresses a critical challenge in urban infrastructure management: financial sustainability. By generating advertising revenue, these smart toilets can partially fund their own operations while maintaining higher standards of cleanliness and functionality than traditional public restrooms.
This approach aligns with China’s broader strategy of leveraging technology to solve urban challenges while creating new economic opportunities. The data collected from these facilities contributes to city-wide analytics platforms that help officials understand traffic patterns, peak usage times, and infrastructure stress points. Similar to how unusual weather phenomena in China capture global attention, these innovative bathroom technologies showcase the country’s willingness to experiment with unconventional solutions to everyday problems.
The success of smart toilet initiatives also demonstrates how China approaches infrastructure investment differently than many Western countries. Rather than viewing public facilities as purely cost centers, Chinese planners increasingly treat them as multi-functional assets that can serve educational, commercial, and data collection purposes simultaneously. This philosophy extends to other infrastructure projects, from entertainment developments to transportation networks.
Public health considerations drive much of this investment as well. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated adoption of contactless technologies in public spaces, and smart toilets equipped with automatic dispensers, voice-activated features, and UV sanitization systems became particularly valuable during health crises. The advertising component helps justify the significant upfront costs associated with installing and maintaining these advanced systems.
Furthermore, these facilities serve as important showcases for Chinese technology companies developing IoT solutions, sensor networks, and urban management software. The toilet installations provide real-world testing environments for technologies that may later be deployed in hospitals, schools, shopping centers, and other public facilities. This creates a feedback loop where successful innovations in public restrooms inform broader smart city development strategies.
The financial model behind advertising-supported smart toilets reflects China’s pragmatic approach to infrastructure funding. Traditional public restrooms require ongoing municipal funding for cleaning, supplies, and maintenance, but smart toilets with advertising revenue can potentially achieve operational self-sufficiency while delivering superior user experiences. This model could influence how other countries approach public facility management and technology integration in urban environments.
Sources:
NDTV, “China’s Public Toilets Require Watching Ads To Get Toilet Paper, Sparking Criticism”
Economic Times, “Pay ₹62 or watch an ad: Now see commercials for toilet paper, striking video shows China’s bizarre restroom marketing twist”
Shanghai University of International Business and Economics, “Research on the innovation strategy of Chinese public toilet business model”
Hurumende, “China’s Smart Toilets Trade Ads for Toilet Paper”
TechSpot, “China is testing restroom machines that make you watch ads in exchange for toilet paper”
Market Report Analytics, “Future Prospects for Public Toilet Information Bulletin Board Growth”
Cognitive Market Research, “The global Toilet market size”
Statista, “Toilet Paper – China Market Forecast”


