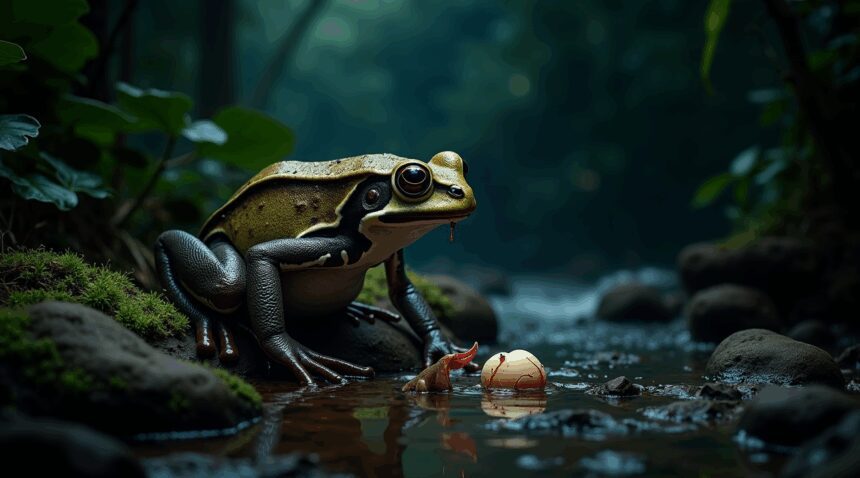
The hairy frog (Trichobatrachus robustus) stands as one of nature’s most extraordinary amphibians, possessing the shocking ability to deliberately break its own toe bones and push the jagged fragments through its skin to create functional claws for defense.
Key Takeaways
- Bone-breaking defense mechanism: The hairy frog can deliberately fracture its toe bones and push the sharp fragments through its skin to create temporary but effective claws when threatened.
- Seasonal “hair” growth: Breeding males develop specialized skin projections along their sides and thighs that increase oxygen absorption by up to 60% while guarding eggs underwater.
- Wide Central African range: The species inhabits six countries across Central Africa, from sea level to 1,458 meters elevation, thriving in fast-flowing rivers and various forest environments.
- Cultural and dietary importance: Local communities, particularly the Bakossi people, harvest these frogs as protein and believe they possess fertility-enhancing properties and celestial origins.
- Conservation concerns despite stable status: While classified as “Least Concern” globally, the species faces localized population declines due to habitat loss, pollution, hunting pressure, and potential disease threats.
Bone-Breaking Defense Strategy
The hairy frog’s bone-breaking defense mechanism operates through a unique anatomical adaptation. Each toe contains a specialized bone structure that can fracture along predetermined weak points when muscles contract with sufficient force. Sharp bone fragments pierce through the skin and extend beyond the toe pads, creating functional claws. Scientists first documented this behavior in laboratory settings where threatened frogs repeatedly deployed their claws against perceived dangers.
These temporary weapons remain effective for several hours before the bone fragments retract and the skin begins healing. Research indicates the frogs can repeat this process multiple times throughout their lives without permanent damage to their skeletal structure. The defense mechanism proves particularly valuable against predators like snakes and birds that attempt to grab the frogs during terrestrial activities.
Seasonal Respiratory Adaptations
During breeding season, male hairy frogs undergo dramatic physical transformations. Hair-like projections, called dermal papillae, sprout along their flanks and rear legs. These structures contain dense networks of blood vessels that dramatically increase the surface area available for gas exchange. Males spend weeks underwater guarding egg masses in fast-flowing streams, making these respiratory adaptations essential for survival.
Studies show these projections can boost oxygen absorption by 60% compared to smooth skin areas. The increased respiratory capacity allows males to remain submerged for extended periods while protecting developing embryos from predators and maintaining optimal water flow around egg masses. After the breeding season concludes, these structures gradually disappear as hormone levels return to baseline.
Geographic Distribution and Habitat
The species occupies diverse habitats across six Central African countries: Cameroon, Democratic Republic of Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Nigeria, and Republic of Congo. Populations thrive from coastal lowlands to mountainous regions reaching 1,458 meters in elevation. Fast-moving streams and rivers provide optimal breeding conditions, while adjacent forests supply abundant terrestrial hunting grounds.
Adults prefer areas with rocky substrates and overhanging vegetation that provide shelter and shade. Juveniles often inhabit quieter stream edges with dense plant cover that offers protection from predators. The species demonstrates remarkable adaptability to different forest types, including both primary and secondary growth areas.
Cultural Beliefs and Human Use
Local communities, particularly the Bakossi people of Cameroon, maintain centuries-old traditions surrounding hairy frog harvesting. Hunters employ specialized techniques to capture these elusive amphibians, often working in teams to drive frogs into nets stretched across stream channels. The protein-rich meat serves as an important dietary component, especially during seasons when other food sources become scarce.
Cultural beliefs attribute various mystical properties to hairy frogs. Traditional healers incorporate frog parts into fertility treatments, believing the species’ remarkable reproductive behaviors translate to enhanced human fertility. Origin stories describe these creatures as gifts from sky beings, explaining their unusual abilities as evidence of divine intervention.
Conservation Status and Threats
Despite its “Least Concern” conservation status, the hairy frog faces mounting pressures across its range. Deforestation removes critical forest habitat while agricultural expansion pollutes waterways with pesticides and sediments. Mining activities, particularly for precious metals, contaminate streams with heavy metals that bioaccumulate in frog tissues.
Overharvesting poses additional threats in areas where demand for frog meat exceeds sustainable collection levels. Climate change alters precipitation patterns that affect stream flow rates essential for successful reproduction. Emerging amphibian diseases, including chytrid fungus, could potentially devastate populations if they spread throughout the species’ range.
Conservation efforts focus on habitat protection and sustainable harvesting practices. Protected areas within the species’ range provide refugia for breeding populations. Educational programs help local communities develop harvesting quotas that maintain population stability while preserving traditional practices.
Future Research and Implications
Research continues to unveil new aspects of hairy frog biology and behavior. Scientists study the biomechanics of claw deployment to understand potential applications in materials science and robotics. Respiratory physiology research examines how dermal papillae could inspire new approaches to artificial gill development.
The hairy frog represents nature’s ingenuity in developing extreme survival strategies. Its bone-breaking defense mechanism and seasonal respiratory adaptations showcase evolutionary solutions to environmental challenges. Understanding these remarkable amphibians provides insights into biodiversity conservation while highlighting the intricate connections between wildlife and human cultures in Central Africa.
The Frog That Breaks Its Own Bones to Fight Back
The hairy frog, scientifically known as Trichobatrachus robustus, possesses one of nature’s most shocking defense mechanisms. When facing danger, this remarkable amphibian deliberately breaks its own toe bones and pushes the jagged fragments through its skin to create functional claws. This extraordinary adaptation represents an extreme form of self-defense that’s virtually unheard of among vertebrates.
An Unprecedented Self-Defense Strategy
Most animals rely on external weapons like teeth, horns, or existing claws for protection. The hairy frog takes a completely different approach by manufacturing its weapons on demand. The process begins when the frog contracts specific muscles in its toes, applying enough pressure to fracture the bones deliberately. These sharp bone fragments then pierce through the toe pads, emerging as temporary but effective claws that can inflict serious damage on potential predators or threats.
This mechanism operates through a sophisticated anatomical structure that allows the frog to control when and how these claws deploy. The bone fragments remain sharp and pointed, making them formidable weapons despite their unconventional origin. Once the immediate threat passes, the claws can retract back into the toes, though researchers are still studying exactly how the healing process works and whether the bones regenerate completely.
The Wolverine Connection and Alternative Names
The resemblance to fictional superhero Wolverine’s retractable claws hasn’t gone unnoticed by scientists and the public alike. This comparison has earned the species several colorful nicknames that reflect its fearsome defensive capability:
- Horror frog – emphasizing the disturbing nature of self-inflicted bone breaking
- Wolverine frog – directly referencing the comic book character’s similar claw mechanism
- Wolf frog – alluding to its aggressive defensive capabilities
These alternative names capture the public imagination while highlighting just how unusual this adaptation truly is. The comparison to Wolverine isn’t just superficial either – both the fictional character and the real frog share the ability to produce claws from within their bodies, though the frog’s method involves actual bone fracturing rather than the metallic claws depicted in comics.
Scientists classify this behavior as an extreme example of autotomy, though it differs significantly from more common forms like lizard tail dropping. While most autotomy involves shedding body parts to escape predators, the hairy frog’s approach actually creates new weapons rather than sacrificing existing anatomy. This represents an evolutionary innovation that pushes the boundaries of what vertebrates will do to survive.
The rarity of this defense mechanism among vertebrates makes the hairy frog a subject of intense scientific interest. Researchers continue studying how this species evolved such an extreme adaptation and whether similar mechanisms might exist in other amphibians that haven’t been discovered yet. The fact that an animal would willingly inflict injury on itself for defensive purposes challenges traditional understanding of pain responses and survival strategies in vertebrates.
Natural selection has clearly favored this dramatic defense strategy in the hairy frog’s environment, suggesting that the benefits of having instant access to weapons outweigh the costs of self-injury. This adaptation likely provides a significant survival advantage in situations where escape isn’t possible and conventional defensive measures would prove inadequate against larger or more aggressive predators.
The hairy frog’s bone-breaking claws represent one of evolution’s most creative solutions to the universal challenge of staying alive in a dangerous environment. By turning its own skeleton into a weapon system, this species has developed a defense mechanism that’s both horrifying and ingenious, earning its place as one of nature’s most unusual creatures.
To learn more, you can watch a fascinating documentary segment here:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vGqZJqYkFVE
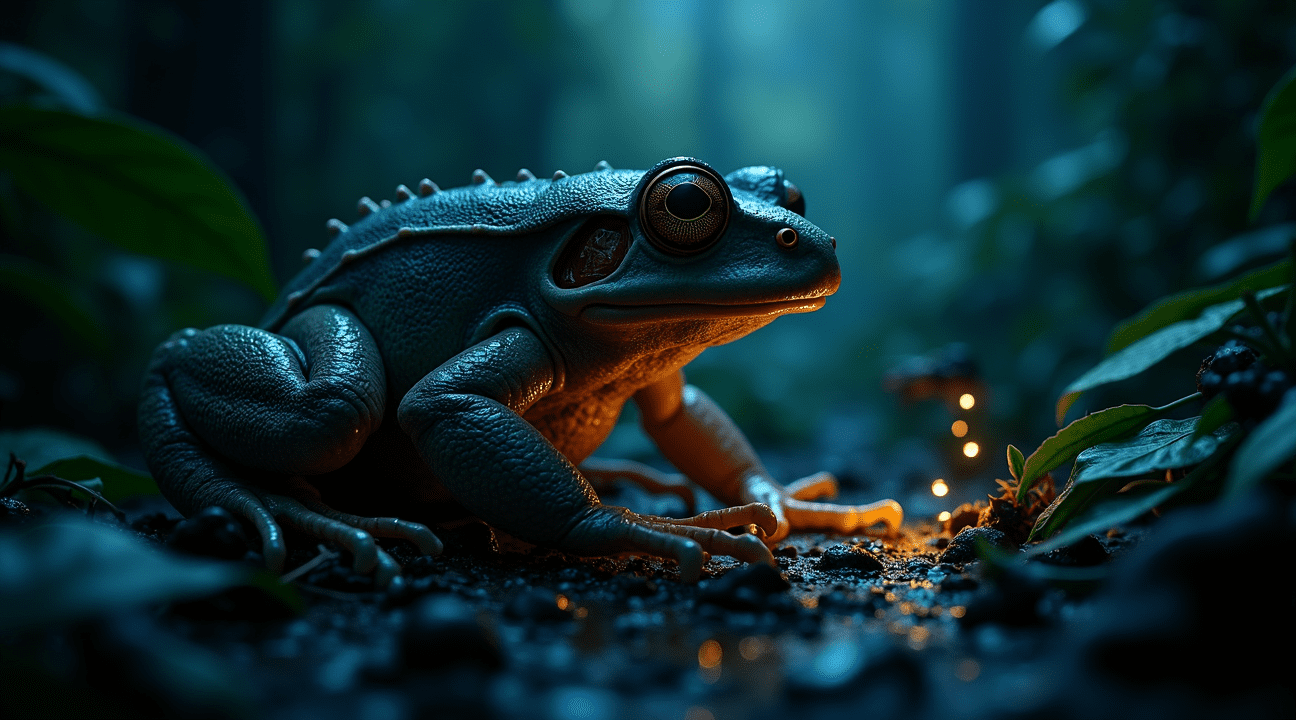

Why Breeding Males Grow ‘Hair’ and What It Really Does
The peculiar hair-like structures that give Trichobatrachus robustus its common name develop exclusively on breeding males during their reproductive season. These aren’t actually hairs at all, but rather elongated dermal papillae—specialized skin projections filled with blood vessels that emerge along the males’ sides and thighs.
Enhanced Oxygen Absorption During Breeding
The primary function of these remarkable structures centers on respiration. When breeding males spend extended periods underwater guarding their eggs, these papillae dramatically increase their skin’s surface area, allowing for more efficient oxygen absorption through cutaneous respiration. This adaptation proves essential since males remain submerged for days or even weeks while protecting their developing offspring.
The increased surface area provided by these skin projections can boost oxygen uptake by up to 60% compared to their non-breeding state. This respiratory enhancement allows males to maintain their vigilant guard duty without frequently surfacing for air, which could leave their egg clutches vulnerable to predators.
Physical Protection for Developing Eggs
Beyond respiratory benefits, males actively use these papillae as protective tools. They wrap the hair-like projections around their egg masses, creating a living shield that helps maintain optimal water flow and temperature around the developing embryos. This behavior also provides physical protection from potential threats and helps prevent the eggs from being swept away by water currents.
Adult males displaying these structures typically measure around 11 cm (4.3 inches) in length. Their bodies showcase an olive-brown coloration with a distinctive dark, black-edged dorsal band running down their backs, while their limbs appear completely black. The contrast becomes even more striking with their bright white undersides.
Female hairy frogs present a different appearance altogether, lacking the dramatic papillae of breeding males. Instead, they display brown speckling patterns across their throats, which helps distinguish them from their temporarily hairy counterparts. This sexual dimorphism becomes most pronounced during breeding season when males develop their full complement of respiratory projections.
The timing of papillae development coincides precisely with breeding activities, demonstrating the evolutionary fine-tuning of this adaptation. Once the breeding season concludes and males no longer need to maintain underwater vigils, these structures gradually recede, returning the frogs to their standard appearance until the next reproductive cycle begins.
Life in Central African Rivers and Forests
The hairy frog makes its home across an impressive stretch of Central African territory. I find it fascinating that Trichobatrachus robustus has established populations spanning six countries: Cameroon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Nigeria, and northern Angola. This wide distribution demonstrates the species’ adaptability to various environmental conditions across the region.
Habitat Preferences and Environmental Adaptations
These remarkable amphibians thrive in diverse forest environments throughout their range. Fast-flowing rivers and streams serve as their primary habitat, though they also inhabit subtropical and tropical moist lowland forests. I’ve learned that they’re equally comfortable in forest edges, plantations, arable lands, and even degraded forests, showing remarkable flexibility in habitat selection.
The elevation range where hairy frogs live is particularly striking. They can be found from near sea level at approximately 26 meters up to mountainous regions reaching 1,458 meters in elevation. This broad altitudinal range suggests the species has evolved to handle varying temperature and humidity conditions across Central Africa’s diverse topography.
What makes their lifestyle particularly interesting is their dual nature. While primarily terrestrial, these frogs maintain a close relationship with freshwater sources. They rarely venture far from rivers and streams, which provide essential moisture and breeding opportunities. This proximity to water sources is crucial for their survival and reproductive success.
The nocturnal behavior of Trichobatrachus robustus adds another layer of complexity to understanding their ecology. These elusive creatures emerge under cover of darkness, making direct observation extremely challenging for researchers. Their secretive nature means much of what we know about their behavior comes from limited field studies and captive observations.
Central African tropical forests provide the perfect backdrop for these unique amphibians. The dense canopy creates a humid microclimate that prevents excessive moisture loss from their permeable skin. Meanwhile, the leaf litter and rocky substrates near streams offer abundant hiding spots during daylight hours.
The association with fast-flowing water appears critical to their survival strategy. These dynamic aquatic environments provide oxygen-rich conditions and may help regulate the temperature fluctuations that could otherwise stress these sensitive amphibians. Additionally, the constant water movement likely supports the diverse invertebrate populations that form the basis of their diet.
Human activities have created new habitats that hairy frogs have successfully colonized. Agricultural areas and plantations now host populations, though whether these environments provide optimal conditions for long-term survival remains unclear. The fact that they can persist in degraded forests suggests some resilience to environmental changes, but this adaptability has limits.
The geographic range encompasses some of Africa’s most biodiverse regions:
- Cameroon’s coastal forests
- Gabon’s pristine wilderness areas
- The Congo Basin’s vast river systems
Each country within their range offers slightly different environmental conditions, potentially supporting genetic diversity within the species.
Stream characteristics play a vital role in determining suitable habitat. Rocky substrates, fallen logs, and overhanging vegetation create the complex microhabitats these frogs require. The combination of terrestrial and aquatic elements in riparian zones perfectly matches their lifestyle needs.
Seasonal variations across their range influence activity patterns and breeding cycles. While tropical climates provide relatively stable conditions year-round, subtle changes in rainfall and temperature affect water levels and prey availability. These environmental cues likely trigger important behavioral responses in wild populations.
The elusive nature of hairy frogs means field researchers must employ specialized techniques to study them effectively:
- Night surveys with appropriate lighting equipment
- Non-invasive habitat monitoring
- Acoustic recording to detect vocalizations
Even with dedicated effort, encounters with these secretive amphibians remain rare events that provide valuable insights into their mysterious lives in Central African waterways.
From Sky Myths to Dinner Plates in Cameroon
The hairy frog holds deep cultural significance in Cameroon, where it represents far more than just another amphibian species. Local communities have woven this remarkable creature into their traditions and daily sustenance for generations.
A Vital Protein Source
Cameroonians rely heavily on hairy frogs as an important protein source, particularly valuing the larger males that can reach impressive lengths of up to 11 inches. These substantial specimens provide considerable nutrition for families and communities throughout the region. Hunters employ traditional methods to capture these frogs, wielding spears and machetes to overcome the creatures’ formidable defensive claws. The hunting process requires skill and caution, as the hairy frog’s bone claws make it one of the more challenging amphibians to harvest safely.
Local hunters have developed specific techniques over time to handle these unique defensive mechanisms effectively. The use of longer implements like spears allows them to maintain distance while ensuring successful captures. This hunting tradition has been passed down through generations, with experienced hunters teaching younger community members the proper methods for safe and efficient harvesting.
Sacred Beliefs and Fertility Traditions
Among the Bakossi people, the hairy frog carries profound spiritual meaning that extends well beyond its nutritional value. Traditional belief systems hold that these remarkable amphibians fall from the sky, creating an almost mythical status for the species within their culture. This celestial origin story has shaped how communities view and interact with hairy frogs for countless generations.
The fertility-promoting properties attributed to consuming hairy frogs represent another crucial aspect of Bakossi traditional belief. Community members often seek out these frogs specifically for their perceived reproductive benefits, making them particularly valuable during certain times of the year or life stages. These beliefs influence harvesting patterns and consumption practices throughout the region.
Cultural ceremonies and rituals sometimes incorporate hairy frogs, reinforcing their importance beyond mere sustenance. Elders within Bakossi communities continue to share these traditional beliefs with younger generations, ensuring the cultural significance of the species remains intact despite modernization pressures.
The intersection of practical nutrition and spiritual significance creates a complex relationship between humans and hairy frogs in Cameroon. This dual role highlights how Central African communities have developed sophisticated understanding of their local ecosystems while maintaining rich cultural traditions.
Harvesting practices must balance community needs with conservation concerns, as the cultural importance of hairy frogs could potentially impact wild populations if not managed sustainably. The species’ unique characteristics and cultural significance make it particularly vulnerable to overharvesting in areas where traditional beliefs drive high demand.
Modern conservation efforts increasingly recognize the importance of working with traditional belief systems rather than against them. Understanding how communities like the Bakossi people view hairy frogs helps conservationists develop more effective protection strategies that respect cultural practices while ensuring species survival.
The contrast between urban and rural perspectives on hairy frogs also shapes conservation approaches in Cameroon. While urban populations may view these amphibians primarily through scientific or conservation lenses, rural communities maintain deep cultural connections that influence their interactions with the species.
Educational initiatives must carefully consider these traditional beliefs when promoting conservation awareness. Successful programs often incorporate respect for cultural practices while introducing sustainable harvesting methods that can meet both nutritional and spiritual needs of local communities.
Climate change and habitat loss pose additional challenges for maintaining both the species and the cultural traditions surrounding them. As environmental conditions shift, the availability of hairy frogs may change, potentially affecting both ecosystem balance and cultural practices that have relied on these amphibians for generations.
Community-based conservation programs show promise for protecting hairy frogs while honoring traditional beliefs. These initiatives recognize that local people often serve as the most effective guardians of wildlife when their cultural and economic needs are respected and supported.
Diet, Reproduction, and Lifespan Secrets
The hairy frog’s carnivorous appetite drives it to hunt a diverse array of prey throughout its forest habitat. This fascinating amphibian doesn’t limit itself to typical frog fare, instead targeting protein-rich invertebrates that provide essential nutrients for survival and reproduction.
Feeding Habits and Prey Selection
Researchers have observed that these frogs demonstrate remarkable hunting versatility by consuming several types of invertebrates. Their diet consists of the following prey items:
- Slugs and terrestrial mollusks that move slowly through leaf litter
- Spiders of various sizes, including both web-builders and hunters
- Myriapods such as millipedes and centipedes found in decaying vegetation
- Beetles ranging from small ground-dwellers to larger forest species
- Grasshoppers and other orthopteran insects during active periods
This varied diet reflects the hairy frog’s adaptability to forest floor ecosystems where prey availability fluctuates seasonally. Their strong jaws and sticky tongues make them effective predators capable of subduing relatively large invertebrates compared to their body size.
Reproductive Cycles and Longevity
Heavy rainfall serves as the primary reproductive trigger for hairy frogs, initiating breeding behaviors that have evolved to coincide with optimal conditions for egg development. When these seasonal rains arrive, females respond by preparing to lay their eggs in carefully selected aquatic environments.
Females deposit eggs in compact clusters that contain between 2 to 23 individual eggs, depending on the female’s size and condition. This relatively small clutch size compared to many other frog species suggests that hairy frogs invest considerable energy into each egg, potentially increasing individual survival rates. The eggs develop in streams and temporary pools created by the rainfall that triggered the breeding season.
Lifespan varies significantly between wild and captive populations. In their natural forest habitat, hairy frogs typically survive for 5 to 10 years, facing predation pressure, environmental challenges, and resource competition that limit their longevity. However, captive specimens benefit from consistent food availability, veterinary care, and protection from predators, allowing them to live up to 15 years under proper husbandry conditions.
The extended lifespan in captivity demonstrates the species’ potential longevity when environmental stressors are minimized. This difference also highlights the various challenges these frogs face in wild ecosystems, from habitat degradation to natural predation cycles that impact their survival rates.
Temperature and humidity fluctuations in their native Cameroon forests can affect both reproductive success and overall health. During dry seasons, hairy frogs may enter periods of reduced activity to conserve energy and water, which influences their metabolic processes and feeding frequency.
Successful reproduction depends heavily on timing, as eggs and tadpoles require specific water conditions to develop properly. If rainfall patterns shift due to climate variations, breeding success can decline, affecting population stability over time. This sensitivity to environmental cues makes the species particularly vulnerable to habitat changes that alter precipitation patterns or water quality in their breeding sites.
The combination of specialized dietary requirements, rainfall-dependent reproduction, and sensitivity to environmental conditions creates a complex life cycle that researchers continue to study. Understanding these patterns helps conservation efforts focus on protecting critical breeding habitats and maintaining the forest ecosystems that support healthy hairy frog populations across their limited range.
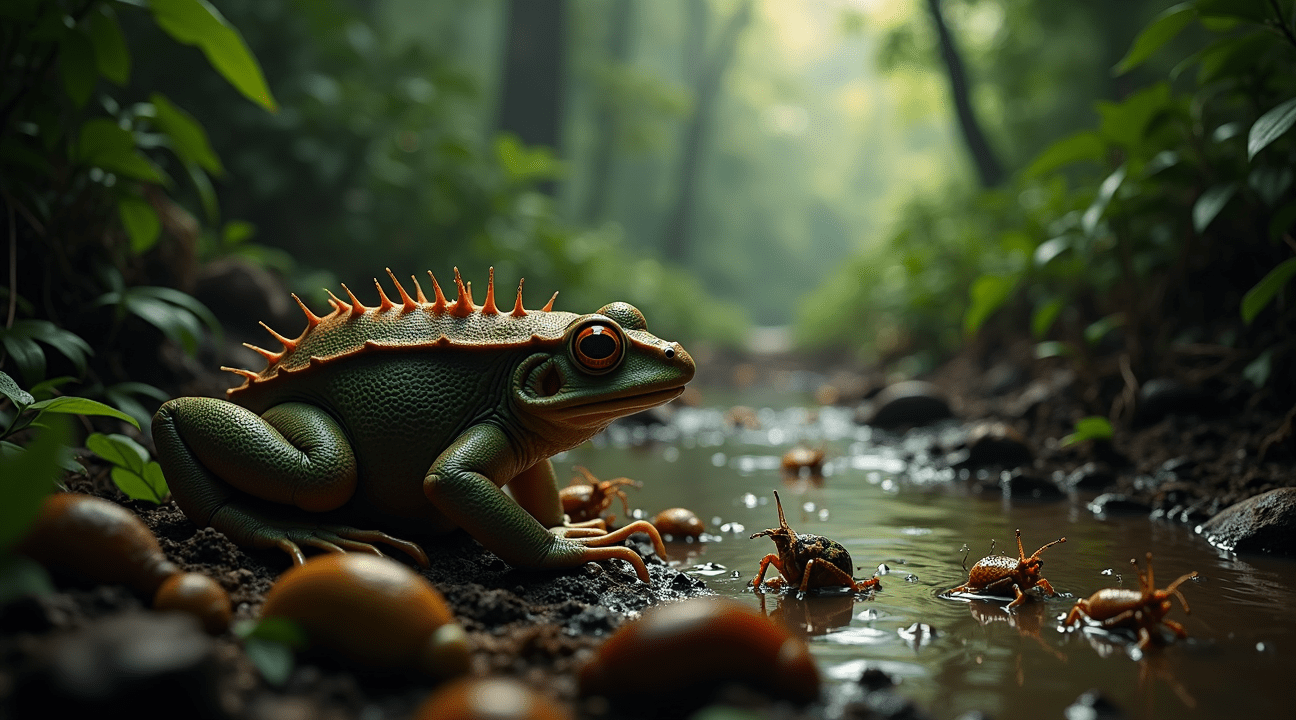

Conservation Challenges Despite ‘Least Concern’ Status
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) currently classifies Trichobatrachus robustus as ‘Least Concern’ on its Red List. This designation might suggest the species faces no immediate threats, but the reality presents a more complex picture that requires careful attention from conservationists and researchers.
Hidden Population Declines
Behind the reassuring global classification lies troubling evidence of localized population decreases across the hairy frog’s range. These declines don’t yet impact the species’ overall survival prospects, but they signal emerging pressures that could escalate if left unaddressed. Field studies in Cameroon and Equatorial Guinea have documented reduced breeding populations in areas where human activities have intensified.
The disconnect between global status and local realities highlights a common conservation challenge — species can lose significant portions of their populations before triggering a change in their official conservation ranking.
Multiple Threats Converging
Several factors contribute to the hairy frog’s declining numbers in specific regions:
- Habitat loss: Deforestation for agriculture and logging operations is fragmenting the dense forests these amphibians call home.
- Pollution: Industrial activities and agricultural runoff contaminate the streams where they breed and develop.
- Hunting pressure: Local communities harvest hairy frogs for food. While the practice has historical roots, increasing human populations and commercial collection have intensified its impact.
- Pet trade: The frogs’ unique appearance makes them attractive in the international exotic pet market.
- Chytridiomycosis: A fungal disease devastating to amphibians globally. Although confirmed cases in hairy frogs are limited, its presence in the region’s amphibian communities poses a significant future risk.
- Climate change: Altering rainfall patterns and rising temperatures in montane forests impact breeding cycles and reduce suitable habitats.
Conservation efforts face the challenge of addressing threats before they reach critical levels. Current monitoring programs remain limited, making it difficult to assess population trends accurately. However, several proactive strategies could help prevent future decline:
- Establishing protected areas within the species’ native range.
- Implementing sustainable harvesting and hunting regulations.
- Increasing disease surveillance and biosecurity measures to manage chytrid risk.
- Expanding community education programs and involving locals in conservation efforts.
The hairy frog’s conservation status serves as a reminder that ‘Least Concern’ doesn’t mean ‘no concern’. Proactive measures taken now could prevent this remarkable species from requiring emergency intervention later.
Sources:
Wikipedia, “Hairy frog”
Biodb.com, “Trichobatrachus – Hairy frog: facts, distribution & population”
Wildverse.space, “Hairy frog-armored mutant of nature or master of survival”
Natural History on the Net, “Hairy Frog”
JSTOR, C. Jones, “Notes on Hairy Frogs (Trichobatrachus robustus Boulenger)”
AmphibiaWeb, “Trichobatrachus robustus”
Nerdist, “Miracles of Weird: The Horror Frog”
Animalia.bio, “Hairy frog – Facts, Diet, Habitat & Pictures on Animalia.bio”

