A rare pink dolphin has captivated global audiences after being filmed by Houston fisherman Thurman Gustin in Louisiana’s Old River Pass during July 2023.
Pink Dolphin “Pinky” Resurfaces in Louisiana
An extraordinary marine discovery has generated excitement among wildlife enthusiasts and marine biologists alike. A pink dolphin, commonly known as “Pinky,” which has resided in Louisiana waters since 2007, was recently filmed by Thurman Gustin, a fisherman from Houston. This sighting occurred in the Old River Pass of Cameron Parish and has encouraged further interest in marine biology and regional eco-tourism.
Background of Pinky
“Pinky” is an albino bottlenose dolphin whose pink coloration stems from albinism—a rare genetic mutation that removes melanin from the skin, allowing visible blood vessels to give the animal its striking color. Not to be confused with the Amazon River dolphin, which naturally has a pink coloration, Pinky stands out as an extremely rare example of albinism among bottlenose dolphins.
New Companion Signals Possible Reproduction
Recent footage captured by Gustin shows a second, smaller pink dolphin swimming alongside Pinky, prompting speculation that the original dolphin may have reproduced. This has raised interest among researchers, who are keen to verify whether the smaller dolphin is Pinky’s offspring.
Key Takeaways
- Thurman Gustin documented the rare pink dolphins in Cameron Parish, Louisiana, providing valuable video evidence.
- “Pinky,” an albino bottlenose dolphin, appears to have been living in the region since 2007 and may have reproduced.
- Albinism causes the pink hue by eliminating melanin, making blood vessels visible through translucent skin.
- The coloration differs from naturally pink Amazon river dolphins, highlighting a rare genetic anomaly.
- The sighting has increased wildlife tourism and awareness of the need for conservation efforts and habitat respect.
Conservation and Tourism Impact
This rare sighting has led to a boost in local tourism, as more people are motivated to witness the unique marine phenomenon firsthand. However, experts emphasize the importance of maintaining respectful distances from the dolphins and adhering to guidelines aimed at protecting critical marine habitats. Organizations actively working in the area encourage responsible viewing practices and provide more information about marine conservation through educational outlets such as the National Geographic website.
Houston Fisherman Captures Extraordinary Footage of Pink Dolphin in Louisiana Waters
I watched in amazement as Thurman Gustin’s extraordinary video footage revealed something truly remarkable in Louisiana waters. On July 12, 2023, the Houston fisherman captured video evidence of a rare pink dolphin breaching in Old River Pass, Cameron Parish, Louisiana. His fishing trip near the Gulf of Mexico turned into a once-in-a-lifetime wildlife encounter that few people ever experience.
Gustin reported seeing not just one, but two pink dolphins during his time on the water. These magnificent creatures appeared in southern Louisiana waters that have become known for recurring dolphin activity. The sighting provides compelling evidence of how these unique marine mammals continue to thrive in the region’s coastal ecosystem.
A Wildlife Phenomenon in Cameron Parish
Cameron Parish has emerged as a notable location for this extraordinary wildlife phenomenon. The area’s position near the Gulf of Mexico creates ideal conditions for dolphin populations, making it a prime location for both regular dolphin activity and these exceptional pink dolphin appearances. Local fishermen and wildlife enthusiasts have begun to recognize the parish as a significant hotspot for marine wildlife observations.
The video evidence from Old River Pass represents more than just a casual wildlife sighting. I find it fascinating how this documentation contributes to our understanding of pink dolphin behavior and habitat preferences in Louisiana waters. These sightings help marine biologists and conservationists track the movements and population patterns of these remarkable creatures.
Significance of the July 2023 Sighting
The timing of Gustin’s discovery adds another layer of importance to this Louisiana wildlife encounter. July 2023 marked a period of increased marine wildlife activity in the Gulf region, and this pink dolphin sighting coincided with other notable marine observations. The return of marine mammals to various waters worldwide highlights the importance of coastal conservation efforts.
Video evidence like Gustin’s footage provides invaluable documentation for researchers studying these rare creatures. The clear visual confirmation helps scientists better understand pink dolphin distribution patterns and their preference for Louisiana’s coastal waters. Each documented sighting contributes to a growing database of information about these extraordinary marine mammals and their habitat requirements in the Gulf of Mexico region.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=otTYgWkYg0Q
Meet “Pinky” – The Local Legend Making Waves Since 2007
Local residents have affectionately dubbed this extraordinary marine mammal “Pinky,” and the dolphin has earned celebrity status throughout Louisiana’s coastal communities. Since first appearing in Calcasieu Lake in 2007, this remarkable creature has captivated both locals and visitors with its distinctive rosy coloration that sets it apart from typical bottlenose dolphins.
Pinky’s story extends far beyond a single sighting. The dolphin has established itself as a permanent resident of Louisiana waters, creating a lasting connection with the community that spans over fifteen years. Regular observers report consistent encounters throughout different seasons, suggesting this area provides suitable habitat for the animal’s long-term survival.
Signs of a Growing Pink Dolphin Family
Recent observations have revealed something even more exciting than Pinky’s continued presence. Witnesses have spotted a larger pink dolphin swimming alongside a smaller companion, raising hopes about potential reproductive success. The size difference between the two individuals suggests the smaller dolphin could be Pinky’s offspring, marking a significant development in this unique population.
These dual sightings represent more than just a curiosity – they indicate that pink dolphins might be establishing a breeding population in Louisiana waters. The presence of what appears to be a calf demonstrates that Pinky has not only survived but potentially thrived in this environment. Such reproductive success would be remarkable for any rare dolphin variant, let alone one with such distinctive coloration.
The relationship between the two pink dolphins continues to fascinate researchers and wildlife enthusiasts. Their consistent appearances together suggest strong social bonds typical of dolphin family units. Mother dolphins typically maintain close relationships with their calves for several years, teaching essential survival skills and social behaviors.
For the local community, Pinky has transcended from marine anomaly to beloved neighbor. Tour operators frequently include potential Pinky sightings in their excursions, while residents share stories and photographs across social media platforms. The dolphin’s regular presence has created an unexpected tourism draw, bringing visitors specifically hoping to glimpse this rare phenomenon.
Photography enthusiasts and marine biologists alike have documented Pinky’s appearances, creating a visual timeline of the dolphin’s life in Louisiana waters. These records prove invaluable for understanding the longevity and behavior patterns of dolphins with leucistic traits. The documentation also helps researchers track any changes in Pinky’s condition or behavior over time.
Pinky’s survival challenges many assumptions about albino or leucistic marine mammals. Traditional scientific thinking suggested that such animals might struggle in wild environments due to increased visibility to predators or potential health complications. However, Pinky’s decade-plus presence demonstrates that these dolphins can adapt successfully to their natural habitat.
The dolphin’s consistent appearances in Calcasieu Lake suggest this location provides optimal conditions for pink dolphins. The area’s rich ecosystem supports abundant fish populations, while the somewhat protected waters offer safety from larger marine predators. These factors may explain why Pinky has chosen to make this region home for so many years.
Conservation efforts have intensified around protecting Pinky and any potential family members. Local authorities emphasize maintaining respectful distances during encounters, ensuring that human interest doesn’t disrupt natural behaviors. Educational programs highlight the importance of preserving marine habitats that support such unique wildlife populations.
Similar to how marine mammals return to familiar waters, Pinky’s loyalty to Louisiana demonstrates the strong site fidelity that dolphins often exhibit. This behavioral trait suggests that protecting specific habitats becomes crucial for maintaining populations of rare marine animals.
Weather patterns and seasonal changes don’t seem to deter Pinky’s presence in the area. Observers report sightings throughout different times of year, indicating the dolphin has adapted well to local environmental variations. This adaptability further supports theories about the animal’s successful integration into the regional ecosystem.
The ongoing story of Pinky continues to unfold with each new sighting, creating anticipation among marine enthusiasts and local residents who eagerly await the next chapter in this remarkable dolphin’s life.
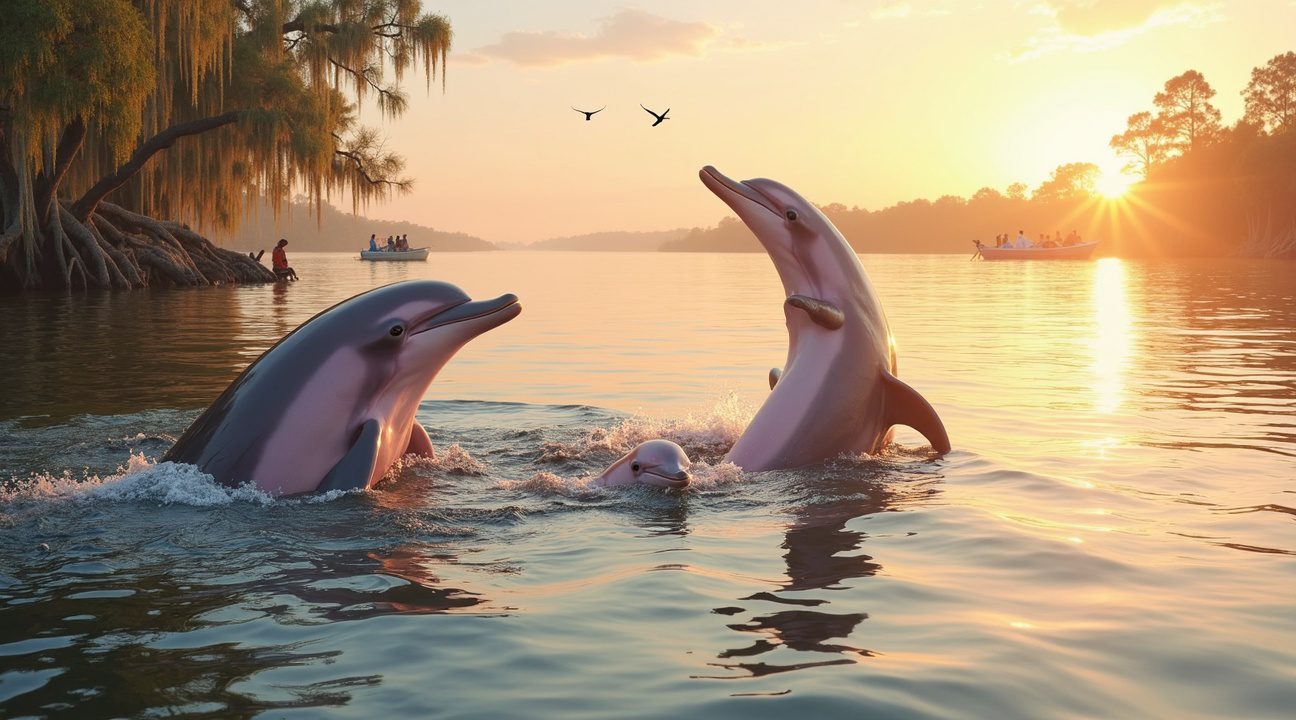
The Science Behind the Pink – Albino Bottlenose Dolphin Revealed
I’ve observed that the Louisiana pink dolphin, affectionately known as “Pinky,” represents a fascinating case of albinism in marine mammals. This remarkable creature is actually an albino bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus), a species that typically displays the familiar gray coloration we associate with dolphins.
Understanding Albinism in Marine Mammals
Albinism creates this extraordinary pink appearance through a complete absence of melanin, the pigment responsible for normal coloration in marine mammals. When I examine Pinky’s distinctive features, several key characteristics confirm the albinism diagnosis:
- Pinkish-white skin tone that contrasts sharply with typical gray dolphins
- Visible blood vessels showing through translucent skin
- Reddish or pink-colored eyes instead of the normal dark coloration
- Complete lack of the usual gray pigmentation found in healthy bottlenose dolphins
The pink hue that gives this dolphin its nickname actually results from blood vessels becoming visible through the translucent, unpigmented skin. This rare genetic mutation affects melanin production entirely, creating a dolphin that appears almost ethereal in Louisiana’s coastal waters.
Bottlenose dolphins like Pinky can grow impressively large, reaching lengths up to 12 feet and weighing as much as 1,400 pounds when fully mature. These powerful marine mammals typically thrive in various coastal environments, but albino individuals face unique challenges due to their distinctive appearance and potential health complications.
The genetic rarity of this condition makes Pinky’s continued survival particularly noteworthy. Albinism in dolphins occurs extremely infrequently, making each sighting scientifically valuable for researchers studying marine mammal genetics and adaptation. Similar rare marine phenomena, like the remarkable return of blue whales to certain waters, remind us how extraordinary marine life can capture our attention and advance scientific understanding.
Researchers continue monitoring Pinky’s behavior and health, as albino marine mammals often experience increased sensitivity to sunlight and may face social challenges within their pods. The translucent skin that creates the beautiful pink appearance also makes these animals more vulnerable to UV radiation damage, potentially affecting their long-term survival in natural habitats.
This exceptional dolphin serves as a living laboratory for understanding how genetic variations manifest in wild marine populations and how these remarkable creatures adapt to life with such distinctive characteristics.

Not to Be Confused with Amazon River Dolphins
The Louisiana pink dolphin represents a completely different phenomenon from the Amazon river dolphin (Inia geoffrensis), which displays pink coloration as a natural characteristic. Amazon river dolphins, commonly called botos, inhabit the freshwater river systems of South America exclusively, while bottlenose dolphins thrive in the marine environment of the Gulf of Mexico.
Key Differences Between Species
Several important distinctions separate these two pink-colored cetaceans:
- Amazon river dolphins naturally develop pink skin as they mature, particularly males during breeding season
- Bottlenose dolphins typically maintain gray coloration throughout their lives, making the Louisiana sighting exceptional
- Botos live exclusively in freshwater rivers and tributaries across the Amazon basin
- Gulf bottlenose dolphins inhabit saltwater coastal areas and open ocean environments
- Amazon river dolphins can reach impressive sizes, weighing up to 352 pounds and stretching 9.2 feet in length
- The genetic mutation causing pink coloration in Louisiana’s bottlenose dolphin creates an extraordinarily rare marine occurrence
Amazon river dolphins maintain stable populations in the tens of thousands throughout South America, though conservationists classify them as ‘vulnerable’ due to increasing environmental pressures. Habitat fragmentation from dam construction and mercury pollution from mining activities pose significant threats to their freshwater ecosystems.
The Louisiana pink dolphin showcases a remarkable genetic mutation within a marine species that doesn’t naturally exhibit pink pigmentation. This genetic anomaly differs drastically from the evolved pink coloration seen in Amazon river dolphins, which developed as an adaptive trait over millions of years in their freshwater habitat. Marine biologists consider such mutations in bottlenose dolphins exceptionally uncommon, making this sighting particularly significant for understanding genetic diversity in Gulf of Mexico populations.
While both species capture attention for their pink appearance, their evolutionary paths, habitats, and the mechanisms behind their coloration couldn’t be more different. The Amazon’s pink dolphins represent a successful freshwater adaptation, while Louisiana’s pink bottlenose dolphin demonstrates nature’s capacity for unexpected genetic variations in established marine populations. Understanding these distinctions helps researchers better appreciate the unique circumstances that led to this rare marine sighting in Louisiana waters.

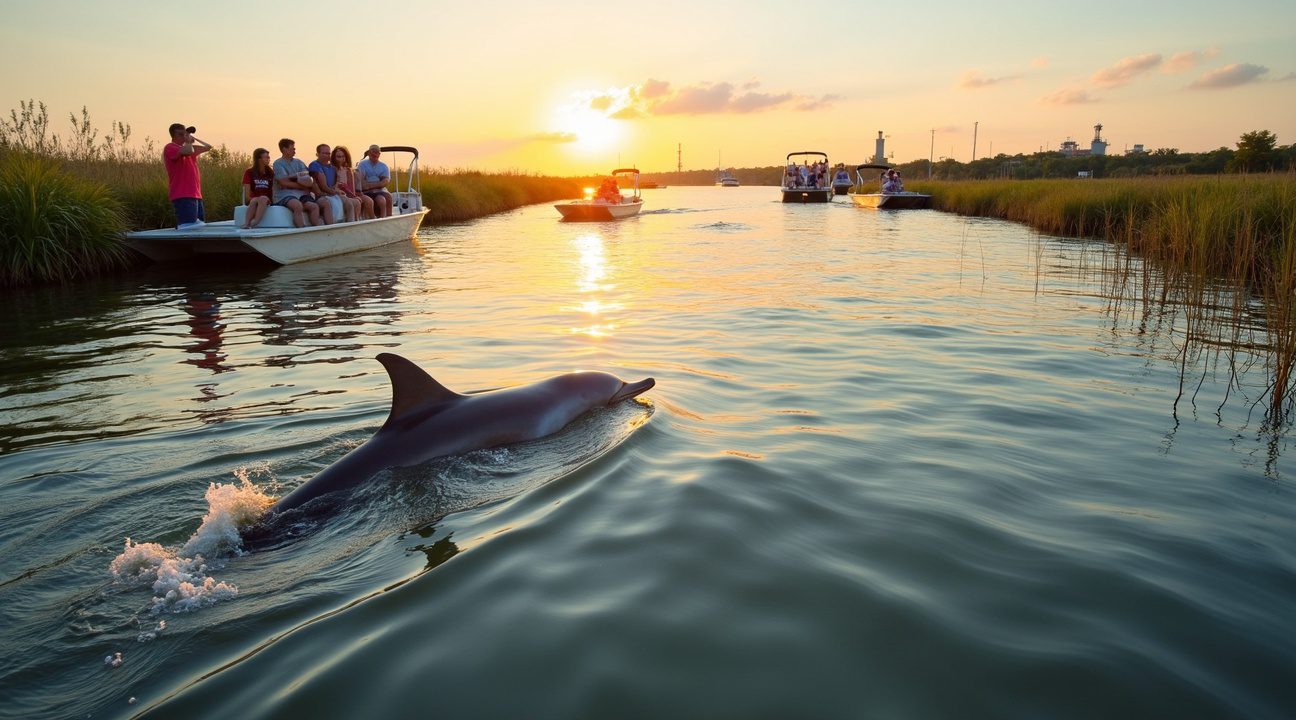
Tourism Attraction Brings Conservation Concerns
Pinky’s remarkable presence in Louisiana waters has transformed the region into an unexpected wildlife tourism destination, attracting visitors eager to witness this extraordinary pink dolphin firsthand. The unique coloration draws photographers, marine enthusiasts, and curious tourists from across the country, creating both opportunities and challenges for local conservation efforts.
Wildlife viewing boats now regularly venture into the areas where Pinky and her pod frequent, hoping to catch a glimpse of this rare spectacle. However, conservationists emphasize the critical importance of maintaining respectful distances during these encounters. Disturbing Pinky or disrupting the natural behaviors of her pod can cause stress, alter feeding patterns, and potentially force the dolphins to relocate to less suitable habitats.
This exceptional sighting serves as a powerful reminder of the marine biodiversity that exists within Louisiana’s coastal ecosystems. The rare pink dolphin phenomenon spotlights the broader conservation needs of bottlenose dolphins and their aquatic environments, particularly as these mammals face increasing pressures from human activities.
Conservation Priorities and Threats
Marine mammal protection efforts must address several interconnected challenges that threaten dolphin populations both locally and globally:
- Tourism impact management requires establishing clear guidelines for boat operators and visitors to minimize disturbance to wildlife
- Wildlife preservation initiatives focus on protecting critical habitat areas where dolphins feed, breed, and socialize
- Environmental threats include water pollution, plastic debris, and chemical runoff that can harm dolphins and their prey species
- Ethical wildlife interaction standards help ensure that tourism benefits conservation rather than compromising animal welfare
Similar rare bottlenose dolphins in other regions have demonstrated the delicate balance between public interest and species protection. Amazon river dolphins, classified as threatened, face comparable challenges from habitat degradation and human interference. These pink freshwater dolphins experience declining populations due to dam construction, fishing practices, and pollution in South American waterways.
The increased attention on Pinky creates an opportunity to educate visitors about responsible wildlife viewing practices. Tour operators can play a crucial role by maintaining appropriate distances, limiting the number of boats in sensitive areas, and providing educational content about dolphin behavior and conservation needs.
Habitat degradation poses a significant long-term threat to dolphin populations throughout the Gulf of Mexico region. Coastal development, oil and gas activities, and agricultural runoff contribute to water quality issues that affect the entire marine food chain. Marine conservation efforts in other regions demonstrate how public awareness can support protective measures for vulnerable species.
The phenomenon of leucism in dolphins, which creates Pinky’s distinctive appearance, occurs rarely in wild populations. This genetic condition reduces melanin production, resulting in the pale pink coloration that makes her so recognizable. Scientists value opportunities to study such unique individuals, as they provide insights into dolphin genetics and population health.
Successful conservation strategies require collaboration between researchers, tour operators, local communities, and government agencies. Establishing marine protected areas, implementing speed restrictions in critical habitats, and monitoring tourism impacts can help ensure that Pinky and her pod continue to thrive in Louisiana waters.
The economic benefits of dolphin tourism can support conservation initiatives when managed responsibly. Revenue from wildlife viewing tours can fund research programs, habitat restoration projects, and educational outreach efforts that benefit the entire marine ecosystem.
Pollution threats extend beyond visible debris to include noise pollution from boat traffic, which can interfere with dolphin communication and echolocation abilities. Chemical pollutants accumulate in dolphin tissues over time, potentially affecting reproduction and immune system function.
Climate change adds another layer of complexity to dolphin conservation efforts. Rising sea temperatures, changing prey distributions, and more frequent severe weather events can alter the coastal environments that dolphins depend upon for survival.

Sources:
CBS News, “Rare pink dolphins spotted swimming in Louisiana”
Wikipedia, “Pinky (dolphin)”
WKYC Channel 3, YouTube Video “Rare pink dolphin spotted in Louisiana waters”
Smithsonian Magazine, “Rare Pink Dolphins Spotted Swimming in Louisiana River”
World Wildlife Fund, “Amazon River Dolphin (Pink Dolphins) | Species”
ABC7LA, TikTok, “Rare Pink Dolphin ‘Pinky’ Spotted in Louisiana”
LA Times, “Pink dolphin — a rare albino — spotted in Louisiana”


