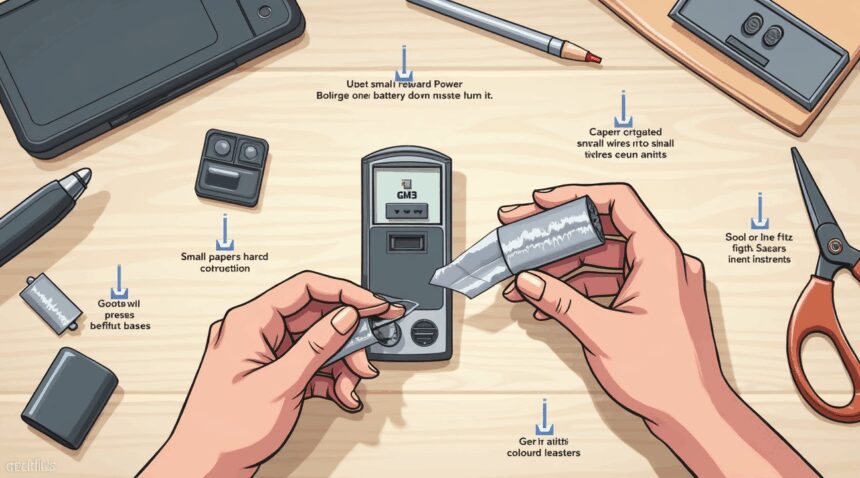
AAA batteries can replace AA batteries in low-power devices through adapters, spacers, or makeshift materials like aluminum foil, despite their smaller size and reduced capacity.
Both battery types deliver the same 1.5V output, but AAA batteries offer significantly less energy (800–1200 mAh vs. 2000–3000 mAh). Physical modifications are required to bridge the approximately 6mm length and 4mm diameter differences when attempting to use AAA batteries in AA compartments.
Key Takeaways
- Commercial adapters provide the safest and most reliable solution for using AAA batteries in AA slots, eliminating connection issues and reducing safety risks compared to DIY methods.
- AAA substitution works best for low-power devices like remote controls, wall clocks, and small LED lights, but fails in high-drain electronics like digital cameras, power tools, and motorized toys.
- Makeshift solutions using aluminum foil or household materials can create temporary fixes but pose safety hazards including overheating, poor connections, and potential device damage.
- AAA batteries deliver 60–70% less energy capacity than AA batteries, resulting in significantly shorter device runtime and more frequent battery replacements.
- Safety monitoring is essential when using any substitution method, watching for excessive heat, battery swelling, unusual odors, or device malfunctions that indicate dangerous conditions.
Additional Resources
For more details on battery specifications and substitution safety, visit BatteryEquivalents.com, a comprehensive resource for battery comparisons and usage tips.
Quick DIY Methods to Make AAA Batteries Fit AA Slots
Commercial adapters offer the most reliable solution for using AAA batteries in AA slots. These plastic or conductive devices bridge the size difference between the two battery types, creating secure connections that maintain proper electrical flow. I find that adapters eliminate guesswork and provide consistent performance across different devices.
DIY Techniques for Emergency Situations
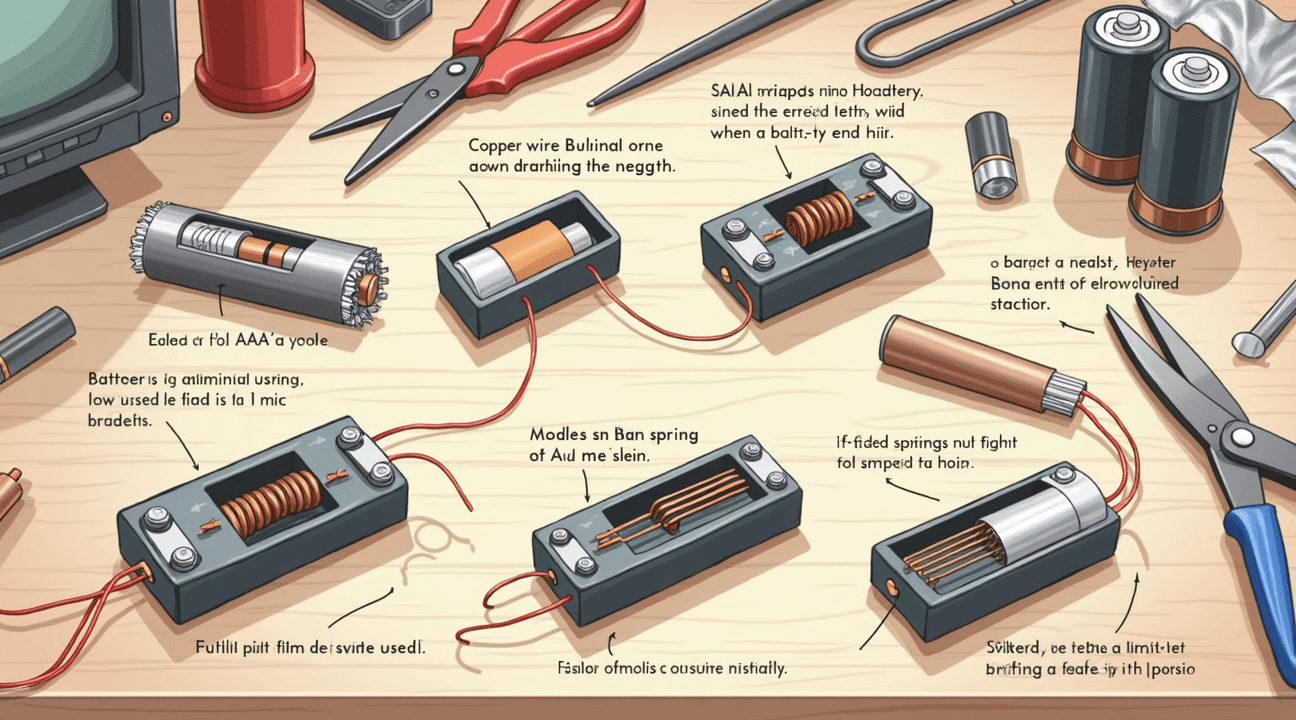
Several household materials can create temporary solutions when commercial adapters aren’t available:
- Aluminum foil wrapped around the negative end of AAA batteries extends their length to match AA dimensions
- Copper wire coiled around battery terminals fills the gap while maintaining conductivity
- Small springs from ballpoint pens can be positioned at battery ends to create proper contact
- Folded paper or cardboard pieces work as non-conductive spacers when combined with conductive materials
The voltage compatibility between AA and AAA batteries makes these modifications technically feasible. Both battery types deliver 1.5 volts, ensuring devices receive adequate power when proper electrical connections are established. This voltage match means electronics won’t experience power-related issues, assuming contact points remain stable.
Creating effective contact requires attention to both positive and negative terminals. I recommend focusing modifications on the negative end, as this typically provides more space for adjustments. The positive terminal’s button-top design usually maintains contact naturally when the battery length is corrected.
Aluminum foil proves particularly effective because it conducts electricity while being easily moldable. Wrapping several layers around the negative terminal creates the necessary extension while maintaining flexibility. The foil should be compressed firmly but not so tightly that it tears when inserted into the battery compartment.
Safety Considerations
Safety considerations significantly impact the viability of DIY modifications. Poor connections can cause overheating, potentially damaging both batteries and devices. Loose materials may create intermittent contact, leading to device malfunctions or unexpected shutdowns. These risks multiply in high-drain devices that demand consistent power delivery.
Device damage represents another concern with makeshift adaptations. Improperly sized modifications can stress battery compartment springs or contacts, leading to permanent deformation. Some devices feature tight tolerances that won’t accommodate wrapped batteries, forcing connections that could damage internal components.
Temperature buildup poses additional hazards with improvised solutions. Inadequate contact creates resistance, generating heat that can affect battery performance and safety. This heat buildup becomes particularly problematic in enclosed devices with limited ventilation.
Effectiveness and Limitations
The effectiveness of DIY methods varies significantly based on device requirements and modification quality. Low-power devices like remote controls often work well with simple adaptations, while high-drain electronics may experience performance issues or refuse to operate. Critical devices should never rely on temporary modifications due to reliability concerns.
Professional repair technicians generally discourage DIY battery adaptations except in genuine emergency situations. The potential for property damage or personal injury outweighs convenience benefits in most circumstances. Commercial adapters cost relatively little compared to potential device replacement expenses.
Long-term use of modified batteries can accelerate wear on device contacts and springs. Repeated insertion and removal of wrapped batteries creates additional friction and stress on battery compartment components. This wear accumulates over time, potentially requiring costly repairs.
Emergency situations may justify temporary modifications despite inherent risks. Power outages, remote locations, or critical device failures sometimes necessitate creative solutions. However, these should remain short-term measures until proper batteries or adapters become available.
Risks of Inconsistent Modifications
Quality control becomes impossible with improvised modifications. Each adaptation differs slightly, creating inconsistent performance across multiple devices. This variability makes troubleshooting difficult when devices malfunction or perform poorly.
Professional adapters undergo testing to ensure safe operation within specified parameters. DIY modifications lack this validation, operating outside manufacturer guidelines and warranty coverage. Device failures resulting from modified batteries typically void warranty protections, leaving users responsible for repair costs.
For a visual explanation of DIY battery fit solutions, consider reviewing tutorials such as this one:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WXyH-j4HkOA
Why Physical Size Matters When Swapping Battery Types
Physical dimensions create the primary obstacle when attempting to substitute AAA batteries for AA batteries in electronic devices. AA batteries measure 50.5mm in length and 14.5mm in diameter, creating a cylindrical volume of 8.3 cm³ and weighing approximately 23 grams. These standardized measurements ensure proper contact with device terminals and secure positioning within battery compartments.
AAA batteries present significantly smaller dimensions at 44.5mm in length and 10.5mm in diameter. This reduced profile results in a volume of just 3.8 cm³ and a weight between 11–13 grams. The 6mm length difference and 4mm diameter reduction mean AAA batteries will rattle around loosely in spaces designed for AA batteries.
Despite their size differences, both battery types deliver identical 1.5V output and share similar chemical compositions, whether alkaline, NiMH, or lithium varieties. This voltage compatibility explains why the substitution concept appears feasible on paper. However, voltage alone doesn’t overcome the fundamental fit issues.
Contact and Connection Problems
Battery compartments rely on precise positioning to maintain electrical contact between battery terminals and device connections. When AAA batteries sit in AA spaces, several critical problems emerge:
- Loose fitting prevents consistent contact between positive and negative terminals
- Battery movement during device operation can interrupt power flow
- Reduced contact pressure may create resistance issues affecting performance
- Vibration or movement can cause complete disconnection
- Spring-loaded contacts may not compress properly with smaller batteries
The diameter difference proves particularly problematic since most battery contacts depend on side pressure to maintain connection. AAA batteries simply can’t fill the space adequately to ensure reliable contact. Even when initial contact occurs, any movement of the device can shift the smaller batteries out of position.
Length discrepancy compounds these issues further. The 6mm gap means AAA batteries may not reach one terminal completely, even when pushed against the opposite end. Spring contacts designed for AA battery compression won’t engage properly with the shorter AAA dimensions.
Weight differences also contribute to stability problems. Lighter AAA batteries move more easily within oversized compartments, increasing the likelihood of losing contact during normal use. Devices designed for the heft of AA batteries may experience unexpected behavior when powered by significantly lighter alternatives.
Professional electronics designers account for specific battery dimensions when creating compartments and contact systems. These carefully engineered spaces can’t accommodate different sizes without compromising functionality and reliability. The standardized nature of battery sizing exists precisely to prevent compatibility issues that could damage devices or create safety hazards.
Some creative solutions involve using adapters, spacers, or conductive materials to bridge size gaps, but these modifications introduce additional failure points and potential safety concerns. Makeshift arrangements rarely provide the secure, consistent power delivery that devices require for optimal performance.
Understanding these physical limitations helps explain why manufacturers produce different battery sizes rather than relying on universal dimensions. Each size serves specific applications where space, weight, and power requirements align with the battery’s characteristics.
Power Performance Differences You Need to Know
I need to clarify the significant energy capacity differences between these battery types before you attempt any substitution. AA batteries deliver substantially more power, with capacities ranging from 2000 to 3000 mAh for alkaline varieties, while AAA batteries provide only 800-1200 mAh. This translates to AA batteries lasting two to three times longer than their smaller counterparts in identical applications.
Current Output Capabilities
Current supply represents another critical distinction that affects device performance. AA batteries typically deliver 1.5-2A of current, making them suitable for high-drain electronics like digital cameras, gaming controllers, and portable radios. AAA batteries supply significantly less current at 0.5-1A, which explains why manufacturers select specific battery sizes for different devices.
Expected Performance Changes
When substituting AAA batteries in place of AA batteries, you may encounter several performance issues:
- Shortened operational life due to reduced capacity
- Potential device malfunctions in high-current applications
- Inconsistent power delivery that may cause intermittent operation
- Possible damage to sensitive electronics expecting stable voltage
- Inability to power motorized components requiring sustained current draw
High-drain devices will experience the most dramatic performance drops since AAA batteries discharge more quickly under demanding conditions. Items like flashlights, toys with motors, or wireless mice may function initially but will require frequent battery changes. Some devices might not operate at all if they require more current than AAA batteries can deliver consistently.
The voltage remains identical at 1.5V for both battery types, so basic compatibility exists from an electrical standpoint. However, the physical size difference creates connection challenges that require makeshift solutions like aluminum foil bridging or battery adapters. These workarounds introduce additional resistance that further reduces already limited performance.
I recommend this substitution only for emergency situations or low-power devices like remote controls or wall clocks. Even then, expect significantly shorter battery life compared to proper AA batteries. For devices requiring reliable, long-term operation, investing in the correct battery size proves more economical than frequent AAA replacements.
Professional electronics repair technicians often advise against such substitutions because the reduced current capacity can stress device circuits designed for AA battery specifications. This stress potentially shortens the lifespan of your electronic devices beyond just the immediate power concerns.
When This Battery Swap Actually Makes Sense
I’ve found that understanding the fundamental difference between AA and AAA battery applications helps determine when substitution becomes practical. AA batteries power digital cameras, toys, large flashlights, and other power-intensive gadgets because they contain significantly more energy capacity. AAA batteries work best for remotes, portable clocks, small flashlights, and compact electronics that require minimal power draw over extended periods.
Low-Power Device Applications
The swap makes perfect sense for specific scenarios where power demands remain minimal. I recommend considering AAA substitution for these situations:
- Remote controls for televisions, air conditioners, or stereo systems
- Wall clocks and small digital displays
- LED keychain flashlights and emergency backup lights
- Wireless computer mice and keyboards during light usage
- Temperature sensors and basic monitoring devices
- Garage door openers for occasional use
These applications typically draw such small amounts of current that the reduced capacity of AAA batteries won’t significantly impact performance. I’ve successfully used this substitution in TV remotes that lasted months with AAA batteries, even though they were designed for AA power cells.
When the Swap Fails
Devices originally designed for AA batteries optimize their circuits for higher capacity and longer run times. Digital cameras represent the worst candidates for AAA substitution because their motors, flash units, and LCD screens demand substantial power bursts. I’ve seen photographers attempt this swap only to experience immediate shutdowns during photo capture.
High-drain toys like RC cars, robotic pets, and electronic games will disappoint users with AAA batteries. These devices expect the 2,500–3,000 mAh capacity that quality AA batteries provide, while AAAs typically offer only 800–1,200 mAh. Large flashlights designed for AA cells won’t achieve their intended brightness levels or runtime specifications with smaller batteries.
Power tools, portable radios, and gaming controllers also fall into the problematic category. I recommend avoiding AAA substitution for any device that heats up during operation, produces sound amplification, or operates motors and moving parts. The voltage drop under load becomes too severe, causing erratic behavior or complete failure.
Emergency preparedness devices deserve special consideration. While a smoke detector might function briefly with AAA batteries, the reduced capacity creates safety risks during extended power outages. I strongly advise against using AAA batteries in any life-safety equipment designed for AA cells.
The physical connection also matters significantly. AAA batteries require aluminum foil, conductive materials, or special adapters to bridge the size gap in AA battery compartments. These makeshift connections can create resistance, further reducing already limited performance. I’ve observed cases where poor connections caused intermittent operation, making devices unreliable when users needed them most.
Consider the cost-effectiveness factor as well. AAA batteries often cost nearly as much as AA batteries despite containing less energy. This means the price per watt-hour becomes substantially higher, making the substitution economically questionable for anything beyond emergency situations.
Smart device manufacturers design their products around specific battery specifications. Modern electronics include power management circuits that monitor battery voltage and capacity to optimize performance. When I substitute AAAs, these circuits may trigger low-battery warnings prematurely or shut down the device to prevent damage from insufficient power delivery.
The substitution works best as a temporary solution rather than a permanent replacement strategy. I’ve found success using AAA batteries to test whether a device functions properly after repairs or to provide emergency power for critical low-drain devices. However, replacing them with proper AA batteries as soon as possible ensures optimal performance and prevents potential damage from inadequate power delivery.
Temperature sensitivity also increases with AAA substitution. Cold weather reduces battery capacity more dramatically in smaller cells, making outdoor applications particularly challenging. I avoid this swap entirely for devices that might experience freezing temperatures or extreme heat conditions.
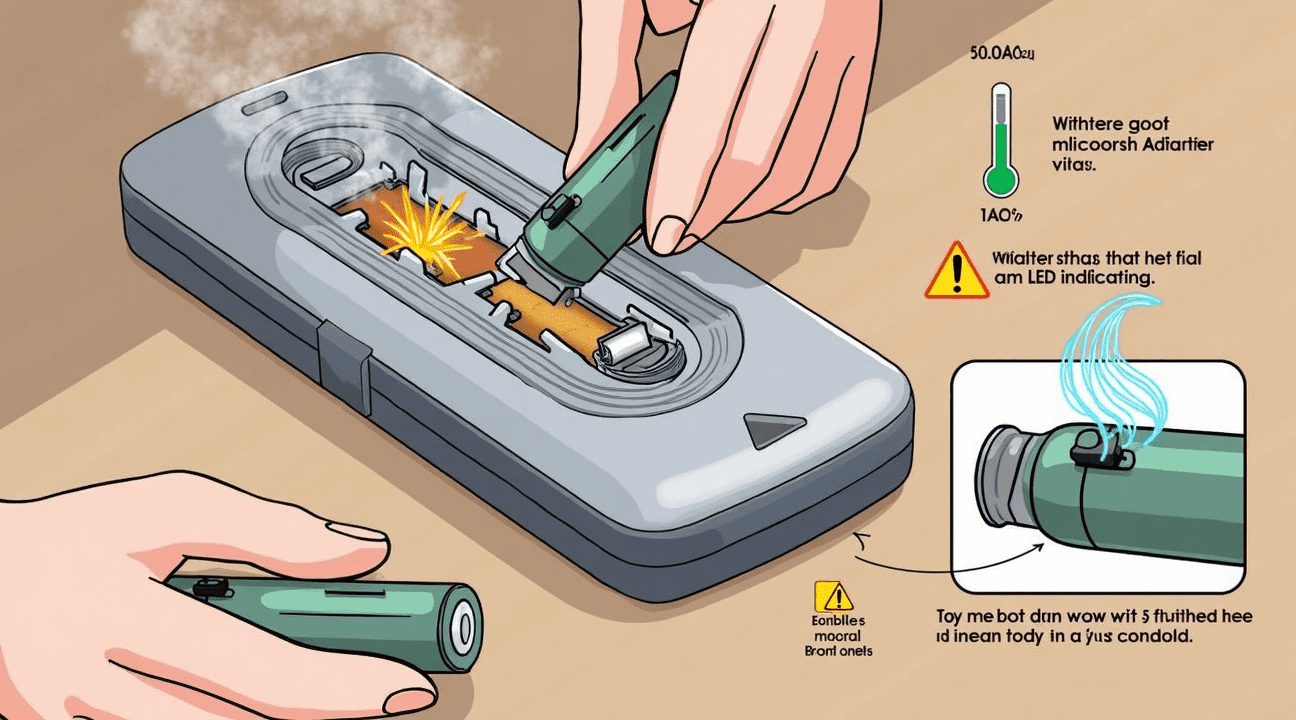
Safety Risks and Performance Issues to Watch For
When substituting AAA batteries for AA batteries, several critical safety and performance concerns demand attention. Understanding these limitations helps prevent damage to devices and ensures safe operation during battery swaps.
Performance Limitations and Device Functionality
AAA batteries deliver significantly reduced run time compared to their AA counterparts due to their lower capacity. Most devices will experience shorter usage periods, requiring more frequent battery changes. High-drain devices face particular challenges, as they may malfunction or shut off unexpectedly when AAA batteries can’t provide adequate power.
Motors in toys or electronic devices often run slower than normal, while LED lights and displays appear dimmer than intended. These performance issues occur because AAA batteries simply can’t sustain the power demands that AA batteries typically handle with ease. Devices requiring consistent, high power output should avoid AAA battery substitution entirely to prevent potential damage or poor performance.
Heat and Connection Hazards
Improvised adapters create serious safety risks that require constant monitoring. Aluminum foil wrapping or other makeshift solutions frequently cause poor electrical connections, leading to short circuits or dangerous overheating. These unstable connections generate excessive heat that can damage both the battery and the device itself.
Overheating poses the most significant safety concern when using adaptation methods. Devices may become uncomfortably hot to touch, and batteries can leak corrosive chemicals or even rupture under extreme conditions. I recommend checking devices every 15-20 minutes during initial use to detect any unusual heat buildup or signs of battery swelling.
Watch for these warning signs during operation:
- Excessive heat from the battery compartment or device housing
- Unusual odors that might indicate chemical leakage
- Visible battery swelling or deformation
- White, crusty residue around battery contacts indicating corrosion
- Device shutting off randomly or behaving erratically
Battery leaks present another serious hazard, as the alkaline electrolyte can cause skin burns and permanently damage electronic circuits. Any signs of moisture or white crystalline deposits around batteries require immediate removal and proper cleanup with appropriate safety equipment.
AAA battery substitution works best in low-power devices like remote controls or digital clocks where consistent high output isn’t critical. However, avoiding this practice in cameras, flashlights, or motorized toys prevents both safety risks and device damage. When AAA batteries must serve as temporary replacements, limit usage time and maintain close supervision throughout operation.
Commercial Adapter Options and Environmental Impact
Several proven adapters make the AAA-to-AA conversion process straightforward and reliable. Three standout options have earned recognition for their performance and durability in various applications.
The PowerPak AAA to AA Battery Converter stands out for its secure fit and consistent power delivery. This adapter maintains proper contact between the AAA battery and the device’s terminals while protecting against loose connections that could damage electronics. Its design accommodates standard AAA batteries without requiring modification or forcing components into place.
Top-Performing Battery Adapters
I recommend considering these proven adapters for reliable AAA-to-AA conversion:
- Eneloop AA Size Spacer – Features precise dimensions and materials that ensure stable power transfer without voltage drops
- GP Batteries AA Adapter – Offers excellent conductivity and fits securely in most AA battery compartments
- PowerPak AAA to AA Battery Converter – Provides consistent performance across different device types and power requirements
These adapters eliminate the guesswork involved in makeshift solutions while protecting both batteries and devices from potential damage.
Both AA and AAA batteries come in rechargeable NiMH versions that significantly reduce environmental impact compared to single-use alkaline alternatives. Rechargeable batteries can be used hundreds of times before requiring replacement, making them a smart choice for frequent battery users. The initial higher cost often pays for itself within a few charging cycles, especially for devices with regular power demands.
Environmental considerations extend beyond just battery type selection. Improper substitutions without adequate monitoring can accelerate battery depletion and place unnecessary stress on electronic devices. When batteries drain faster than expected, users often replace them more frequently, creating additional waste streams. Device wear increases when power delivery remains inconsistent, potentially shortening the lifespan of expensive electronics.
Monitoring power levels becomes crucial when using AAA batteries in AA slots. The reduced capacity means shorter operating times, but tracking usage patterns helps prevent unexpected shutdowns that could cause data loss or device malfunctions. Regular checks ensure optimal performance while extending the useful life of both batteries and devices.
Proper battery recycling plays a vital role in minimizing environmental impact regardless of battery type or adapter use. Many retailers and municipalities offer collection programs specifically designed for spent batteries, preventing toxic materials from entering landfills. These programs handle both alkaline and rechargeable batteries, making responsible disposal convenient for consumers.
Choosing rechargeable options wherever possible represents the most effective strategy for reducing long-term environmental impact. Modern NiMH rechargeable batteries maintain their charge longer than earlier generations and can be recharged even when not fully depleted without suffering memory effects. This flexibility makes them practical for emergency kits, remote controls, and other devices where batteries might sit unused for extended periods.
The combination of quality adapters and rechargeable batteries creates a sustainable solution for AAA-to-AA conversion needs. Adapters eliminate the need for makeshift solutions that might damage devices or waste batteries through poor connections. Rechargeable batteries reduce the total number of batteries consumed over time while providing reliable power for years of use.
Smart battery management includes rotating stock to ensure fresh batteries remain available when needed. This practice becomes especially important when mixing battery types or using adapters, as different batteries may have varying discharge rates. Keeping track of installation dates and performance helps identify when replacements become necessary before complete failure occurs.
Quality adapters justify their cost through improved reliability and device protection. Cheap alternatives might save money initially but could lead to connection problems, power interruptions, or even device damage that costs far more than premium adapters. Investing in proven products from established manufacturers provides peace of mind and consistent results across different applications.
Sources:
Holobattery, “Differences Between AA and AAA Batteries”
Batteries Store, “Difference Between AA vs AAA Batteries”
UfineBattery, “Understanding the Difference Between AA and AAA Batteries”
Allelco, “AA vs AAA Batteries: Which Is Better for Your Needs?”
Battery Specialists, “4 Differences Between an Alkaline Battery AAA and a Lithium Battery AAA”
Batteries Inc, “Comparison of AA, AAA, C, and D Batteries”
Wikipedia, “AAA battery”